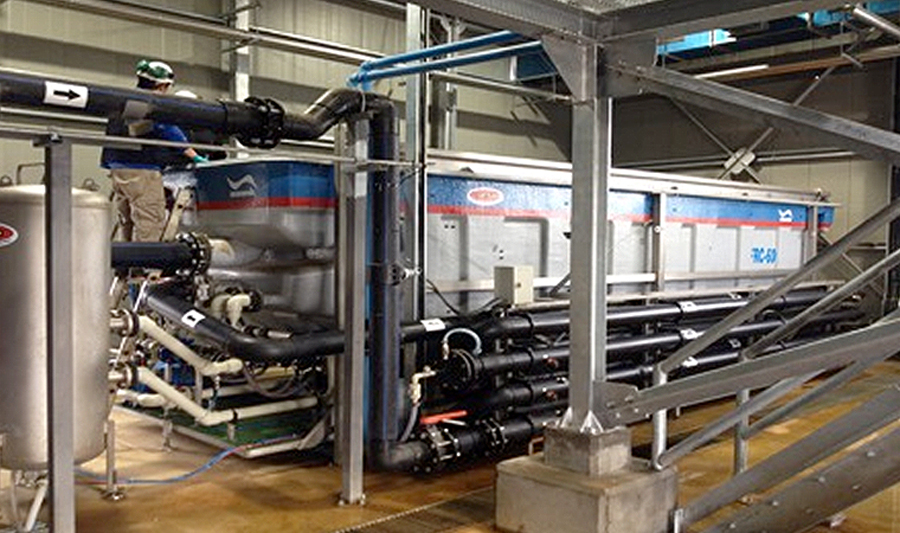
This system is considered highly efficient for different uses in water treatment, but it stands out for the removal of solids in the preliminary stage of wastewater treatment plants, especially for the separation of solids, settleable and suspended, oil and grease. and hydrocarbons.
This industrial wastewater treatment system is an efficient solution for:
- Sewage treatment
- By-product recovery
- Recirculation and reuse of water
Industries in which it is recommended to use the DAF system to treat their waste.
Water is a vital service that requires economic management. The DAF industrial water treatment system allows you to solve a problem in process and waste water.
Some examples of the production processes especially indicated for this type of treatment system are:
- Slaughterhouses
- Meat industry
- Fish processing industry
- Dairy industry
- Precooked foods
- Margarine production
- Treatment of oils and fats
- Canning industry
- Industrial kitchens
- Fast food producers
- Soap production factory
- Cosmetic industry
- Textile industry
- Chemical industry
- Petrochemical industry
- Iron and steel industries
- Metallic manufactures
- Galvanization
- Soil recovery
- Waste management
- Urban wastewater treatment
Characteristics of DAF waste treatment systems
The residual water is pumped at a constant flow to the coagulation-flocculation process, entering the flocculator. The flocculator equipment is usually a tube specially designed for this task. Here a coagulant is dosed just before the static mixer, which provides the necessary surface inside the pipe for the reaction to occur. Coagulation is the destabilization of suspended and/or colloidal particles in wastewater. The result is the separation of solids from the water to form micro-flocs that generally have a positive electrical charge.
Subsequently, a flocculant is injected into the pipe, just before the second static mixer. The flocculant is a polymer of opposite charge that attracts positively charged micro-flocs. Flocculation is the agglomeration of micro-flocs that increase the size of the floc (macroflocs) making flotation possible by injecting dissolved air into it.
Immediately after coagulation-flocculation, the flocculated wastewater is injected into a stream of clarified water, which is recirculated from the DAF. This water is supersaturated with air bubbles. These micro-bubbles adhere to the flocs forming particles with a lower density than water, producing flotation in the DAF system.
After the addition of chemicals (coagulants) to the DAF, a pH adjustment prior to entering the system is also considered in the same way as that used in the equalizer, that is, a pH sensor connected to a dosing system , but in this case only basic.
In the flotation process, the artificial fixation of air bubbles on the solid particles occurs, this gives them a very fast rate of ascent to the particle-gas assembly, which is formed.
Flotation will be at least 5 times faster than conventional decantation. The system also allows agglomerates of gas particles to form which, as clusters, form groups that double the initial ascensional speed. The result is rapid removal of solids loading.
The raw water is mixed with a stream of recycled water from the outlet compartment. The treated water is recirculated through a special pump to an air saturation system at 4 kg/cm2 pressure. By application of Henry's Law, when this current passes at almost atmospheric pressure, the saturated water dissipates the excess air. A studied system of injectors distributes this flow in the float and causes the pressure jump so that the size and quantity of the micro-bubbles is adequate to achieve maximum adhesion-adsorption of the impurities.
The agglomerates of air and particles rise to the surface of the float where continuous dehydration takes place, before being discharged by the surface scraper into the collector. The scraper is driven by a motor variator. Heavy particles, such as sand, remain in the sedimentation compartment, built at the bottom. A pneumatically actuated valve removes the formed sludge which, through a sandbox, returns to the homogenization or to the head of the plant.
The removal of floated sludge can be done by simple gravity, since the sludge outlet is placed at a height of 1m, and whenever necessary the float can be raised by means of brake shoe to be able to remove said sludge without the need for pumping.
EXPERIENCE OF ECOPRENEUR IN IMPLEMENTATION OF DAF SYSTEMS
Ecopreneur has developed and implemented projects in different types of industries and production processes with excellent results.
Application examples in which Ecopreneur has participated are shown in the table below:
| BUSINESS | Flow (m3/h) | Flow (m3/day) | Category |
| Greenplast | 180 | 4.320 | Plastics Recycling |
| La Estrella (Agrosuper) | 140 | 3.360 | Animal production and meat processing |
| Cial | 100 | 2.400 | Animal production and meat processing |
| Lácteos del Sur | 90 | 2.160 | Dairy products |
| Marine Harvest | 90 | 2.160 | Fish and salmon processing |
| Cermaq (Ex Agroindustrial Santa Cruz) | 90 | 2.160 | Fish and salmon processing |
| La Ramirana (Agrosuper) | 90 | 2.160 | Animal production and meat processing |
| CCU Coinco | 90 | 2.160 | Bottler |
| Colun Columela | 60 | 1.440 | Dairy products |
| Colun | 60 | 1.440 | Dairy products |
| Fitz Roy | 60 | 1.440 | Fish and salmon processing |
| Yadrán | 45 | 1.080 | Fish and salmon processing |
| Lechera del lago | 30 | 720 | Dairy products |
| Nestlé | 20 | 480 | Dairy products |
| ICB | 20 | 480 | Food production |
| Campanario | 10 | 240 | Thermoelectric |
| Team Food | 10 | 240 | Production of oil and others |
| TOTAL | 1.185 | 28.440 |
If you need more information about this system and its application to your production process, contact us and one of our experts will gladly advise you.